Electro-stimulation & traditional exercise burn 30% more calories
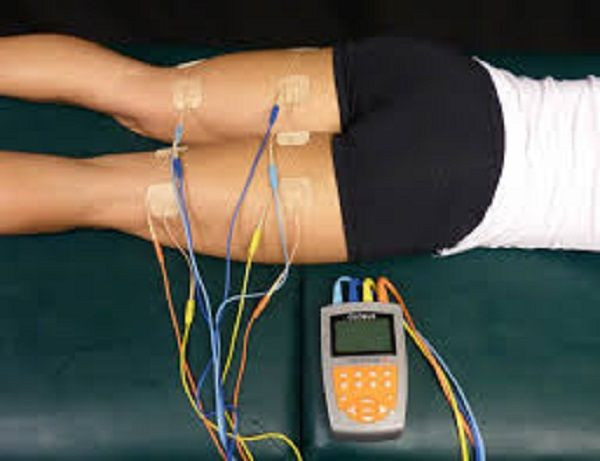
A study by researchers at the University of Granada in Spain recommends combining traditional exercise with electro-stimulation to burn more calories by up to 30 percent. It not only increases caloric burn but also helps boost performance.
The study, published in the Andalusian Journal of Sports Medicine, assessed 262 people after a bout of high-intensity interval training (HIIT), followed by a session of electro-stimulation. The combination generated up to 30 percent higher calorie burn than doing aerobic exercise alone, reports the American Council on Science and Health.
But the study stresses it should be used in tandem with exercise, not as a substitute. It offers different neurological, metabolic and functional advantages such as increasing the metabolic rate for several days after the workout, meaning the body continues to burn calories. In contrast, conventional aerobic activity generates lower calorie usage which happens only while the exercise is ongoing, explains MDLinx.
High-intensity workout with electrical muscle stimulation resulted in higher levels of lactate concentration in the blood, at 15.6 mmol.L-1, in comparison to only 2 mmol.L-1 for aerobic exercise. There was also significant differences in basal oxygen consumption at 60 minutes and 24, 48 and 72 hours after the different kinds of workout.
Angel Gutierrez Sainz, physiology professor at the university, recommends 20-minute weekly HIIT sessions with electro-stimulation for sedentary people, elite athletes suffering from an injury and sportsmen in training.
Two previous papers cite the benefits of electro-stimulation. A 2013 paper, published in Applied Physiology Nutrition and Metabolism journal, says it induces boost in energy expenditure similar to exercise. Another study, published in Physical Therapy, says electro-stimulation improves muscular strength and helps in rehabilitation.





















