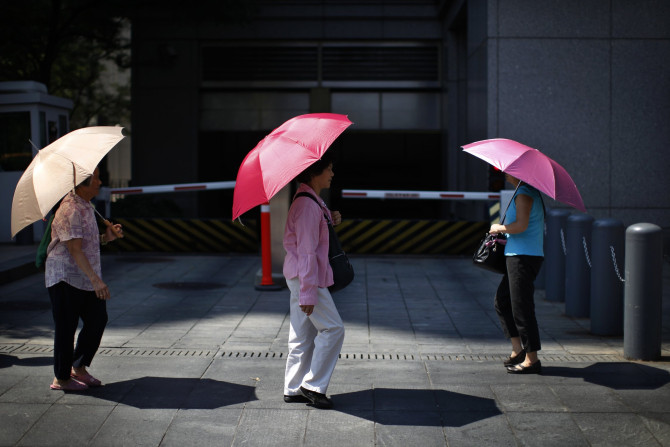
A new study has predicted that climate change will put New Yorkers at the risk of overheating. The study has predicted thousands of heat deaths by 2080. If no steps are taken to reduce emissions and adapt to warming, as many as 3,331 people may die every year in New York alone by 2080. By that time, the number of hot days is going to triple, and that would cause heat deaths due to respiratory conditions, heart problems, dehydration and heat exhaustion.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 24, 2016
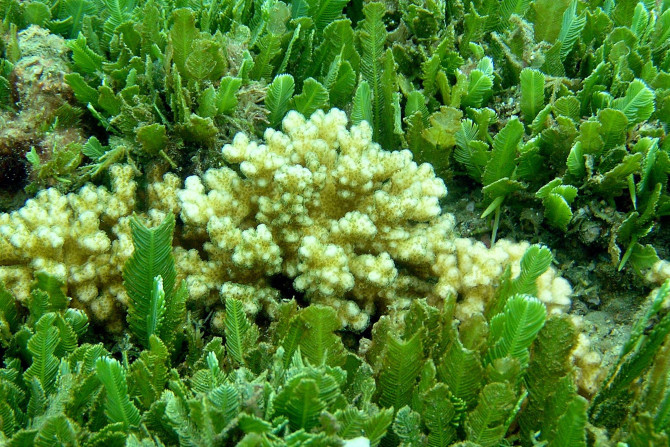
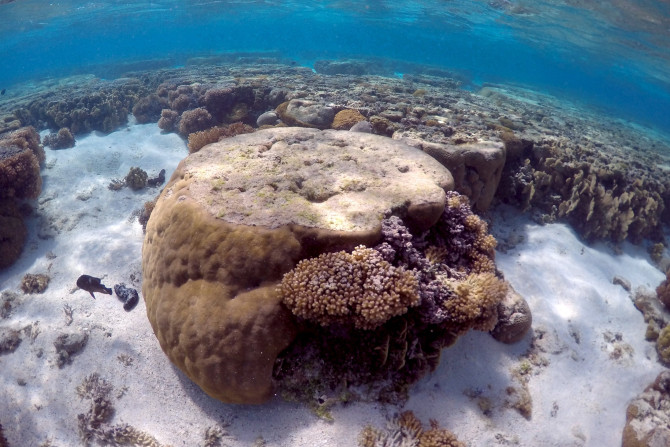
In a study that has brought relief to scientists and conservation experts, researchers have identified genes in algae that may allow corals to survive in high ocean temperatures. The genes in algae may stop coral bleaching that has rendered most of Australia’s Great Barrier Reef lifeless.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 23, 2016
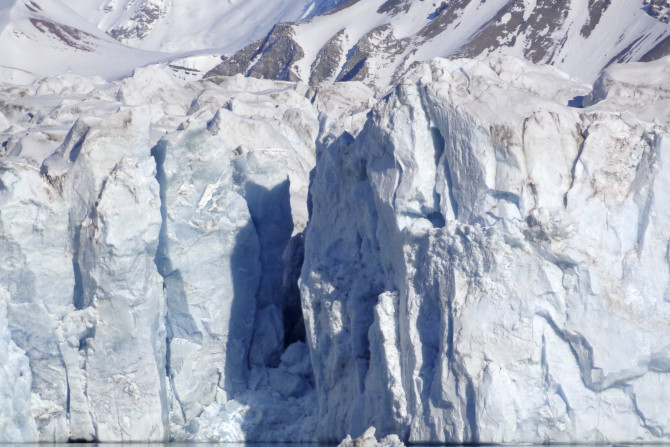
A study has revealed that fields of pink-coloured algae are forming on world’s glaciers and it is accelerating global warming. Previously, the experts thought the pink colour of the snow was caused by some chemical spill or baby seal clubbing.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 23, 2016
In an outcome to a University of Sydney study on shark attacks, Perth people have stood beside the deadly sea creatures and have opted for non-lethal approaches to stop the attacks. They have spoken against culling of sharks even after two consecutive shark-related deaths rattled Australia earlier this month.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 22, 2016
A new study has revealed that one of the most-endangered lichens in the world, Boreal felt lichen, may decline 50 percent in 25 years despite conservation efforts. Researchers have called for increased protection as Atlantic Canada’s federally protected Boreal felt lichen is losing out to human-induced climate change.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 22, 2016
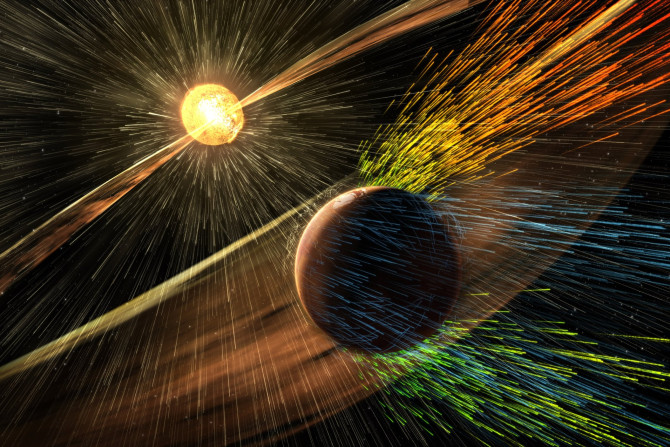
NASA has reported that an “electric wind” can strip Earth-like planets of oceans and atmosphere. The statement came after it was found out that planet Venus has an electric wind that is strong enough to remove components of water from its upper atmosphere.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 21, 2016
Eyeless catfish have been discovered in a Texas cave and experts believe that they may have come from Mexico. Blind fish, though documented in 1954 in Mexico, have never been seen this far north.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 20, 2016
University of Chicago researchers have made a horrifying discovery. They were comparing shells of live mussels taken from the Pacific coast with historical mussel shells, some more than 1,000 years old. They came to a horrifying realisation. Mussel shells are getting thinner and thinner and it’s bad news for the species.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 19, 2016
After over 6,000 reef surveys in 46 countries, Australian researchers are extremely excited as they have found 15 areas in damaged world reefs that are heaving with fish. The scientists have named these areas “bright spots,” as they have can prove to be instrumental in developing exciting coral reef conservation solutions.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 19, 2016
Scientists have detected life-giving gas oxygen in a faraway galaxy, 13.1 billion light years away. This could well be the oldest oxygen ever detected in the universe. The galaxy in question, SXDF-NB1006-2, is causing a storm in the scientific kingdom. Scientists are seeing the galaxy as it was 700 million years after birth of the universe. It shows the oldest signs of oxygen and this has baffled scientists.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 18, 2016
Victoria-based aquatic scientist Sheree Marris filmed what was a giant spider crab aggregation on the shores of Port Phillip Bay. The “spectacular” sight of giant spider crabs gathering up in Australian waters was a unique experience for the marine scientist as she had never seen something like this before.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 18, 2016
New study has revealed that climate change and human impact played a crucial role in the extinction of South America’s giant beasts such as sloths the size of elephants, one-tonne bears and sabre-toothed cats. Megafauna happily existed along with humans for nearly 3,000 years. However, as the climate rapidly warmed up, they became extinct within 300 years.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 18, 2016
The mosaic-tailed rat, popularly known as the Bramble Cay melomys, has been declared extinct by Queensland researchers. These rats were a resident of an island in Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Researchers believe that the reason for their extinction is manmade climate change.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 15, 2016
Scientists from Southampton University, UK, have found the most unique way to constrain carbon dioxide emissions, and that is to turn them into stone. The researchers found this smart way to cut emissions in the midst of global warming while working in Iceland.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 14, 2016
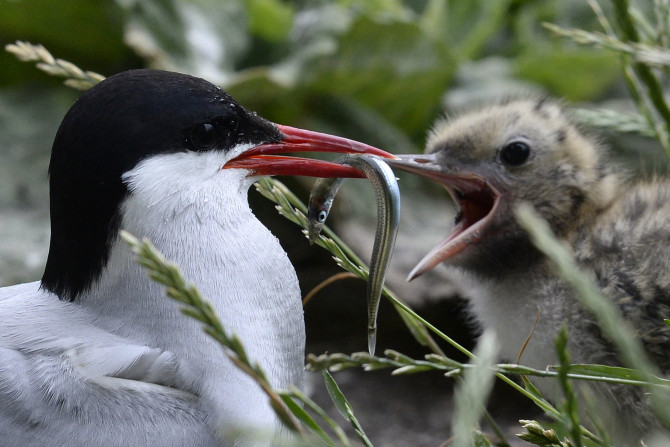
An Arctic tern, which measures 11-15 inches in length and weighs about a 100 grams, has set the record straight for the longest migration trip ever recorded. As Arctic terns can live for 15 to 30 years, they can cover over three million kilometres over its lifetime, which is roughly equivalent to four round trips to the moon.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 09, 2016
WWF-Australia recently released shocking images and a video of the impact of coral bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef. The once colourful and vibrant reef that attracted thousands of tourists worldwide has been reduced to a shady brown with slimy algae impacting the World Heritage Site like never before.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 07, 2016
Researchers from Uppsala University have found that larval fish exposed to microplastic particles display stunted growth and changed behaviour. Quite interestingly, the fish prefer eating the microplastic particles than plankton.
Ritwik Roy
Jun 04, 2016
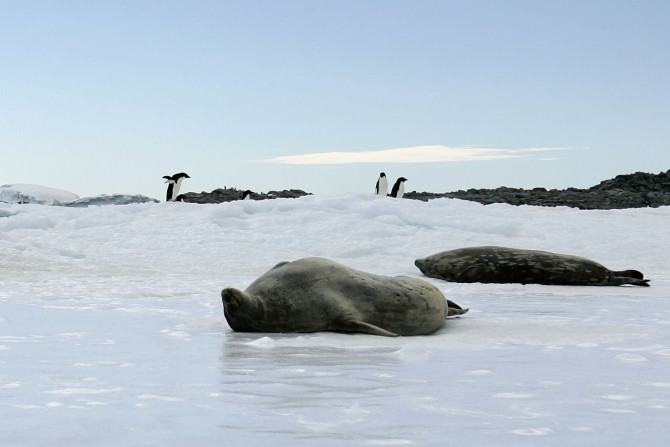
Antarctica is far less affected by climate change than the Arctic. North Atlantic’s cold and deep ocean currents dull the effects of global warming and even slow down sea level rise.
Ritwik Roy
May 31, 2016
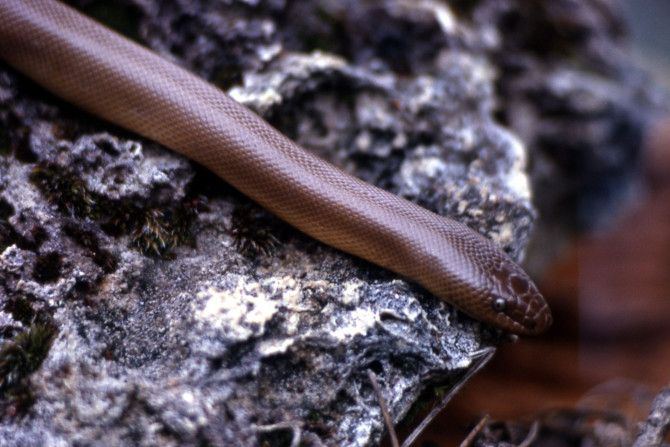
Dr. Graham Reynolds from the University of North Carolina Asheville led a team of researchers into the Bahamian Archipelago only to discover a new species of boa in the remote Conception Island Bank.
Ritwik Roy
May 30, 2016
Henry Marr from Mount Vernon, Washington, is extremely upset as he believes people are wrecking the planet. The kid broke down after he saw a video of animals eating plastic trash.
Ritwik Roy
May 30, 2016
Coral bleaching in certain northern and central parts of Australia’s Great Barrier Reef has killed off more than 35 percent of the corals, extensive aerial and underwater surveys have revealed.
Ritwik Roy
May 30, 2016
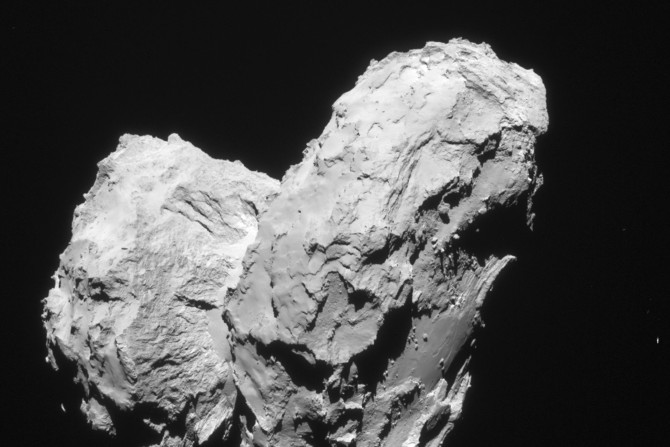
European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta spacecraft discovered ingredients glycine and phosphorous on a comet that are regarded crucial to the origins of life. Comets delivered chemical building blocks of life to Earth.
Ritwik Roy
May 29, 2016
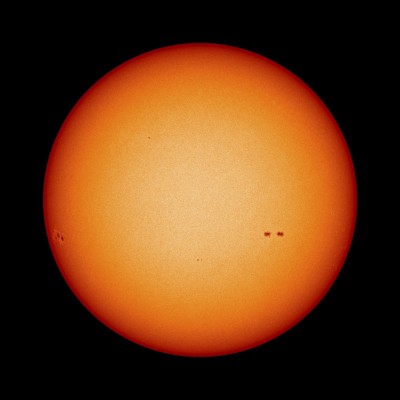
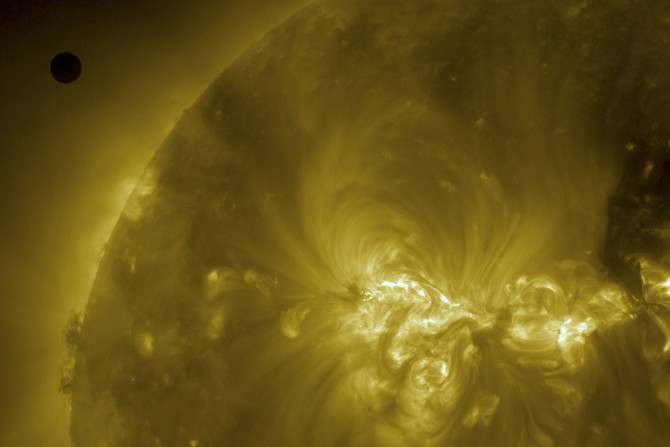
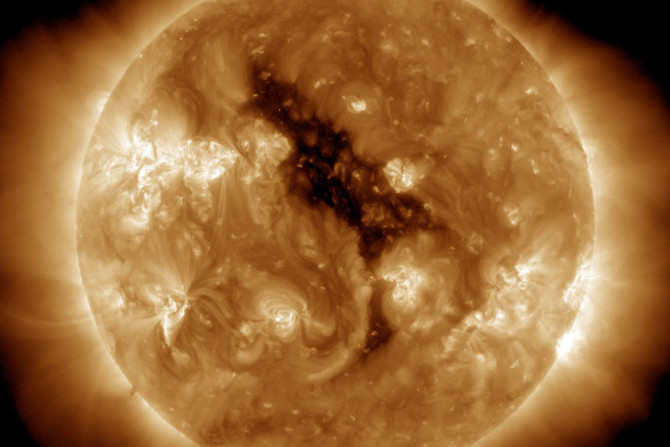
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) recently captured a massive hole on the sun’s surface. The gigantic coronal hole is blasting radioactive solar particles towards Earth.
Ritwik Roy
May 28, 2016
The new algorithm enables scientists to pinpoint the tsunami source that in turn helps scientists in predicting the impact of the waves once they hit the shores.
Ritwik Roy
May 26, 2016
A new study has revealed that feeding cows with antibiotics may increase greenhouse gas emissions from cow dung, burps and farts.
Ritwik Roy
May 25, 2016
The final report by the Great Barrier Reef Water Science Taskforce has put forward major concerns regarding the reef’s water quality. Water quality improvement measures till date have been slow.
Ritwik Roy
May 25, 2016
Researchers drone technology to track shark behaviour along coastal waterways. The drones can not only protect beachgoers, they can also allow experts learn more about shark behaviour and their environment.
Ritwik Roy
May 25, 2016
Four billion years ago, Earth received only 70 percent of sun’s energy than what it receives today and should have been like an ice ball. Yet it was warm with liquid water.
Ritwik Roy
May 24, 2016
Burning all fossil fuels would make Earth so hot that global temperatures would soar by eight degrees. It would release five trillion tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Ritwik Roy
May 24, 2016
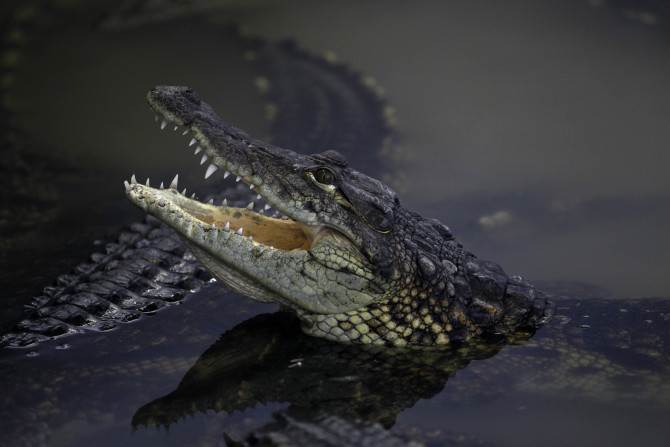
The Nile crocodiles can grow up to a length of 18 feet. They caused 123 fatalities in Africa and at least 480 attacks on humans between 2010 and 2014.
Ritwik Roy
May 23, 2016