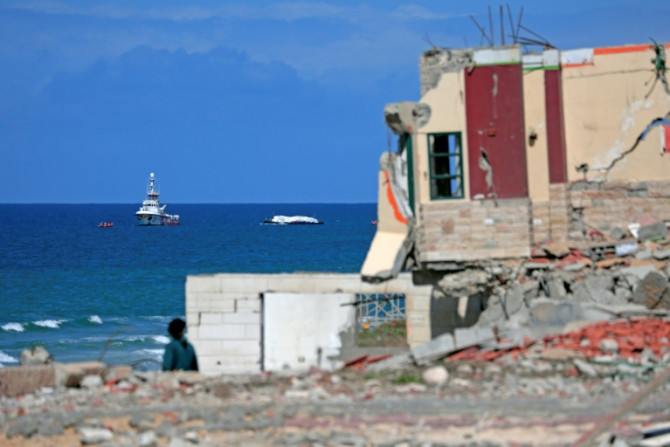
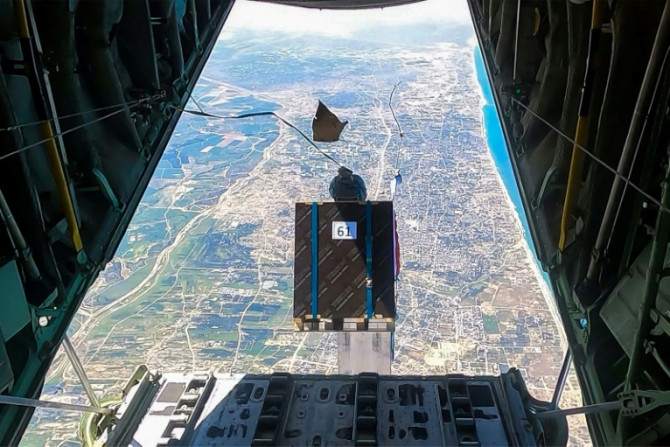
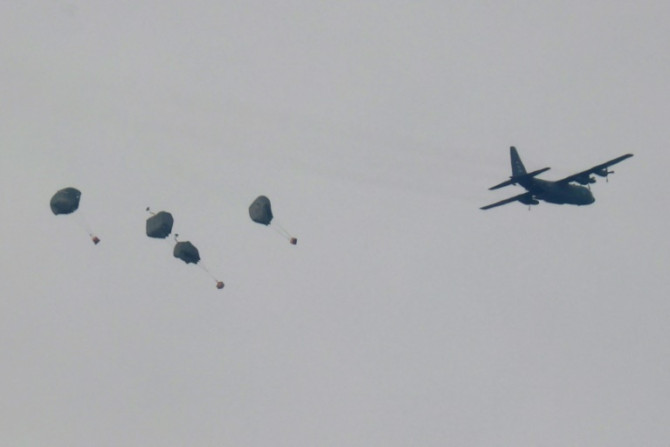
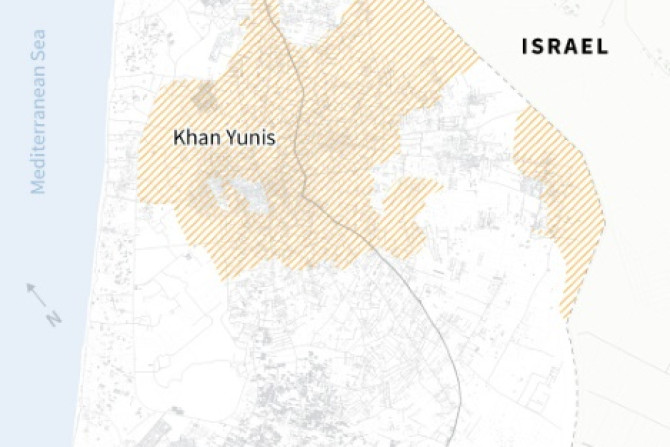
With the humanitarian situation in Gaza increasingly desperate, donors are considering delivering relief supplies from the sky, as the UN warns famine is "almost inevitable".
Mar 02, 2024
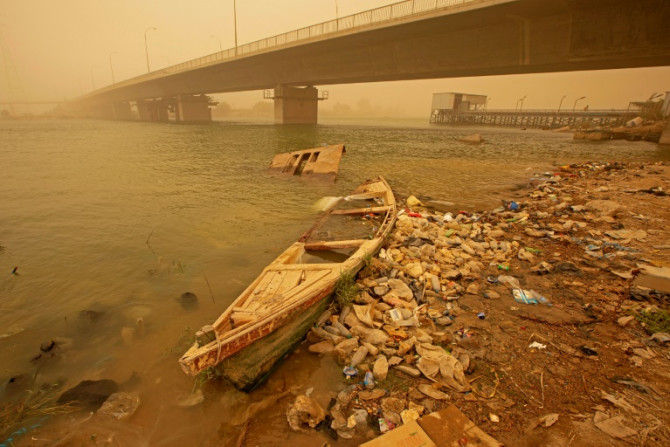
Iraq enjoys tremendous oil wealth but many hard-scrabble farmers in the north say crude spills have contaminated their lands, piling on pressure as they already battle drought.
Feb 27, 2024
A new ceasefire between Israel and Hamas could start as soon as Monday, US President Joe Biden said, in a deal that could include the exchange of dozens of hostages held in Gaza for several hundred Palestinian detainees.
Feb 27, 2024
Israel's military proposed a plan Monday for "evacuating" civilians from the Gaza Strip, after Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said a ground invasion of the Palestinian territory's southern city Rafah was necessary for "total victory".
Feb 26, 2024
Israel's war cabinet has discussed the next steps for negotiations towards a hostage deal and ceasefire in its war with Hamas, as concern deepens over the increasingly desperate situation faced by civilians in the devastated Gaza Strip.
Feb 25, 2024
In a shift from tit-for-tat tariffs and strong-arm tactics to tech restrictions and investment curbs, US policy towards China has become more targeted under President Joe Biden -- though still hardline.
Feb 25, 2024
Animal activists have fashion brands squarely in their sights this Milan Fashion Week, hoping to pressure Italian brands Max Mara and Fendi to give up fur in future collections.
Feb 23, 2024
In the shade of a sacred tree, Indigenous wise men chew coca leaves as they mull the threats to their home among the melting, snow-capped peaks of Colombia's Sierra Nevada mountains.
Feb 22, 2024
Foreign ministers of the G20 group of nations open a two-day meeting Wednesday in Brazil, with a bleak outlook for progress on a thorny agenda of conflicts and crises, from the Gaza and Ukraine wars to growing polarization.
Feb 22, 2024
Stricken by drought and depleted by upstream dams, Iraq's once mighty rivers the Tigris and Euphrates are suffocating under pollutants from sewage to medical waste.
Feb 21, 2024
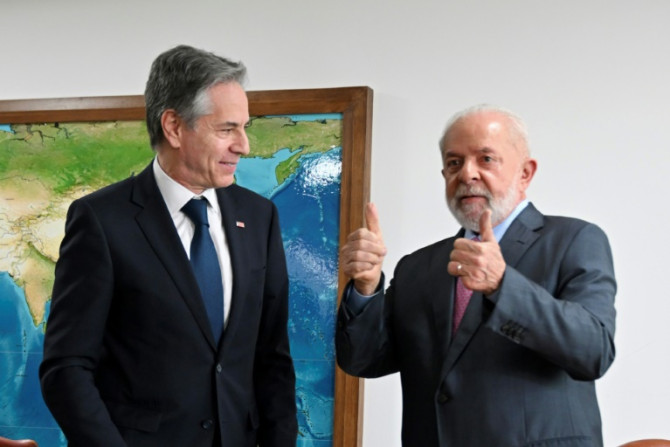
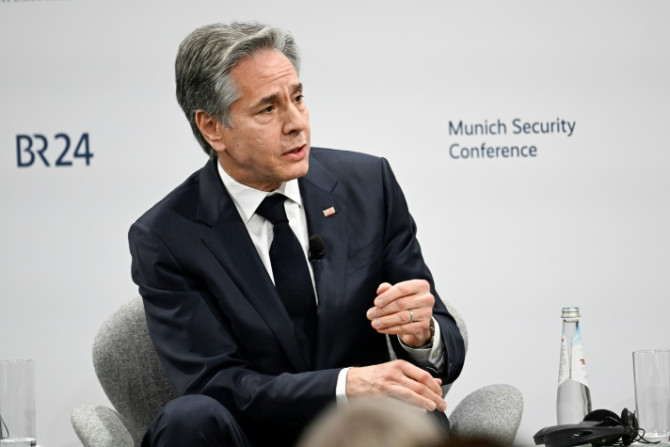
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken landed in Brazil on Tuesday for his first trip to the South American nation, arriving amid a diplomatic spat after President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva enraged Washington ally Israel by comparing its Gaza campaign to the Holocaust.
Feb 21, 2024
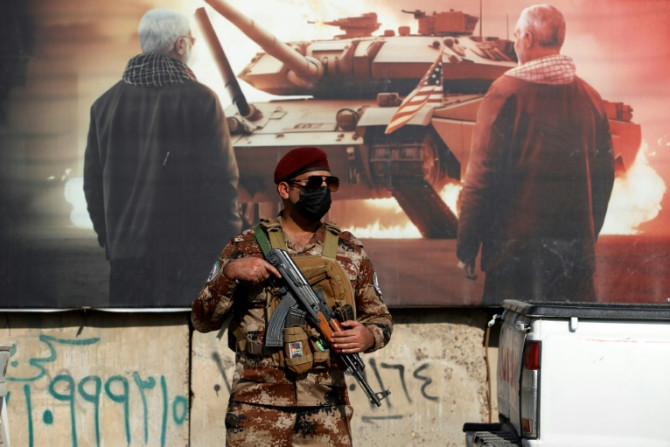
Israel has threatened to invade Gaza's Rafah by the start of Ramadan if Hamas does not return the remaining hostages by then, despite international pressure to protect Palestinian civilians sheltering in the southern city.
Feb 19, 2024
A climate of fear pervades a hospital in the occupied West Bank city of Jenin, where patients and doctors are reeling from last month's deadly raid by Israeli agents disguised as medics.
Feb 17, 2024
African leaders open a two-day summit on Saturday as the continent wrestles with coups, conflicts, political crises and regional tensions.
Feb 17, 2024
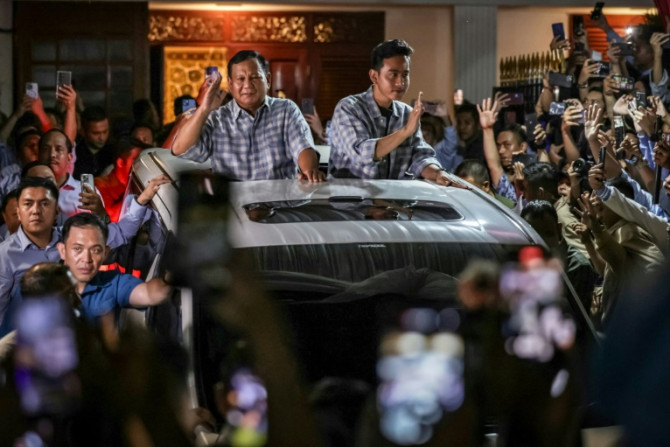
Once a feared general under late dictator Suharto, Indonesia's likely new president Prabowo Subianto now faces the challenge of honouring his campaign pledges to maintain the country's economic growth.
Feb 15, 2024
Chile is embarking on a European hunt for investors in solar, wind and green hydrogen technologies as it looks to decarbonise copper mines and other industries reliant on fossil fuels.
Feb 12, 2024
Earth has endured 12 consecutive months of temperatures 1.5C hotter than the pre-industrial era for the first time on record, Europe's climate monitor said Thursday, in what scientists called a "warning to humanity".
Feb 09, 2024
As waves from the Arabian Sea crash into the shores of Pakistan's port city of Karachi, election candidate Ahmad Shabbar tells voters a list of growing but often ignored climate threats.
Feb 06, 2024
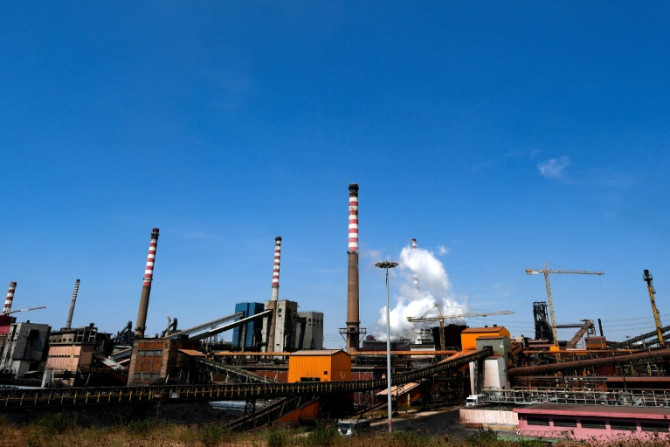
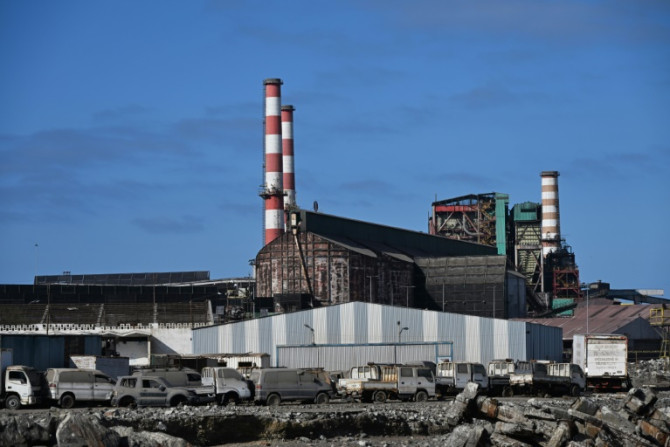
Doctor Maria Grazia Serra's patients have been "breathing, eating and drinking" toxins from Taranto's steelworks for decades, but a dispute over the vast Italian plant could finally see its ecological conversion.
Feb 06, 2024
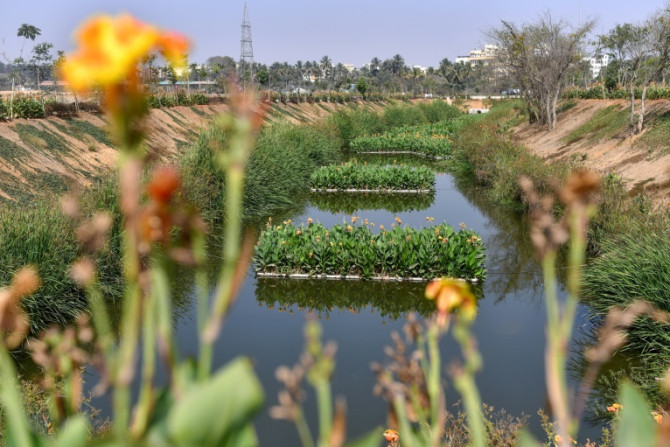
Ancient lake systems once provided Bengaluru with critical water supplies, but the Indian tech hub's breakneck expansion left many waterways covered over or used as dumps.
Feb 06, 2024
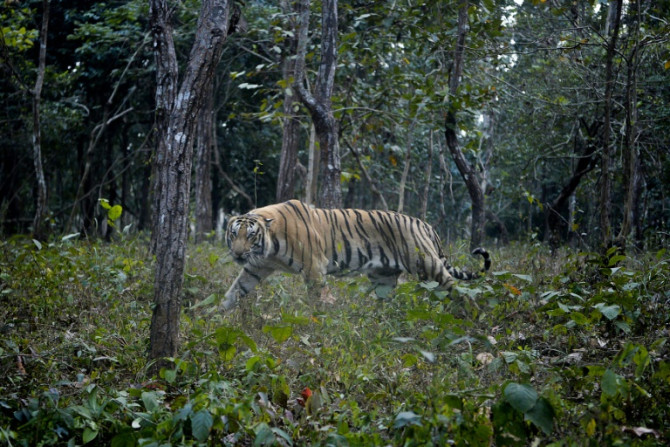
Tigers in India have been photographed in high-altitude mountains rarely seen before, with experts suggesting relentless human pressure and a heating climate are driving them from traditional hunting grounds.
Feb 06, 2024
Britain's King Charles III, whose cancer diagnosis was announced on Monday, has thrown himself into the role of monarch since ascending to the throne nearly 17 months ago.
Feb 06, 2024
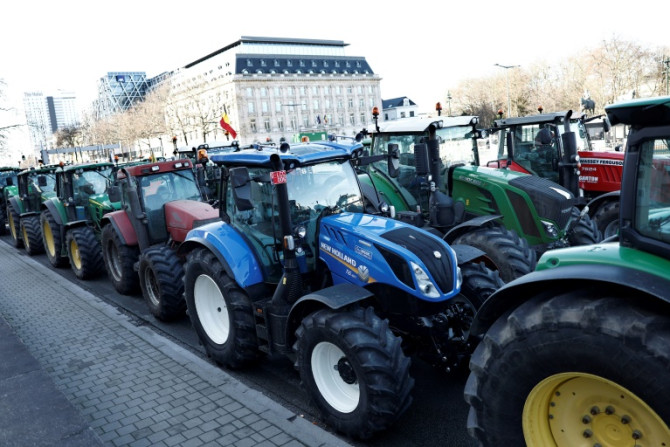
The EU's climate goals for 2040 are set to further dial up the pressure on a farm sector that has yet to get tough on greenhouse gas emissions -- but is already up in arms over existing environmental rules.
Feb 06, 2024
Scorching summer heat is hard to imagine now in mid-winter Paris, but in six months' time when the world's athletes arrive for the Olympics, another pounding heatwave would spell trouble for organisers.
Feb 05, 2024
After a drone attack killed three American soldiers in Jordan on Sunday near the Syrian and Iraq borders, Washington immediately accused "radical Iran-backed militant groups operating in Syria and Iraq".
Jan 31, 2024
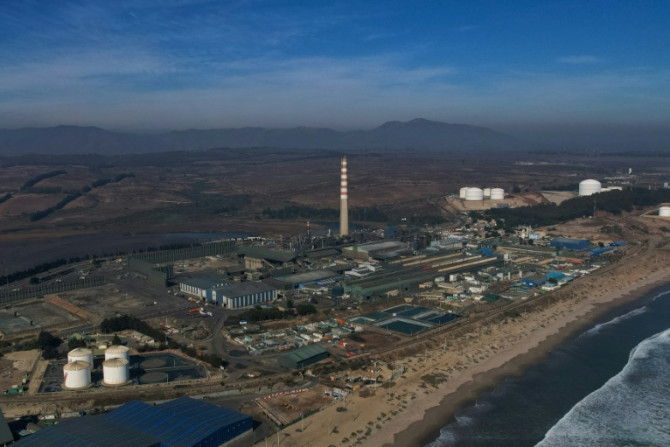
Vultures soar above the mining town of Tocopilla, where Chile's dizzying transition away from coal-fueled energy has left dozens of workers idle and unsure of their future.
Jan 31, 2024
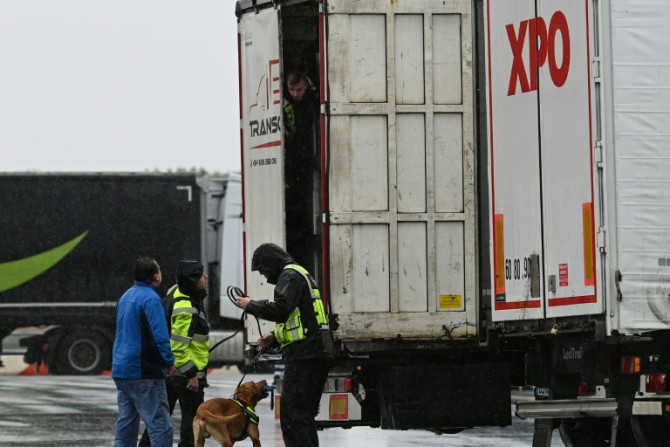
The UK will finally roll out post-Brexit border checks Wednesday on food, plant and animal products imported from the European Union, fanning fears of more price hikes, empty shelves and even Valentine's Day flower shortages.
Jan 30, 2024
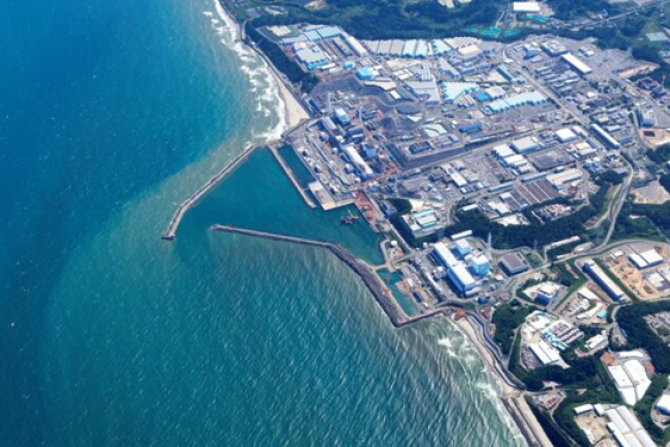
Initial official statements and findings from authoritative organizations confirmed the absence of harmful radioactivity levels in both water and fish.
Tedfuel
Oct 10, 2023
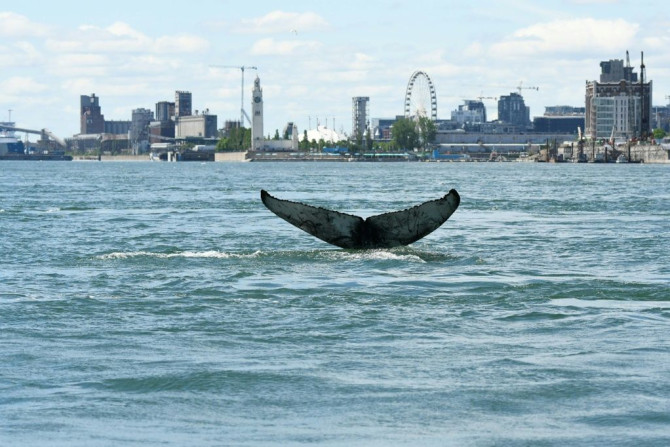
A humpback found itself in a crocodile-infested river and Australian authorities are working on leading it back to open water.
Savannah Tee
Sep 14, 2020
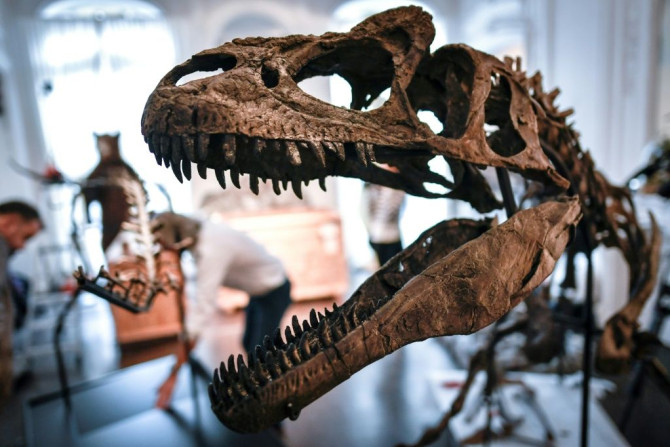
Giant carnivorous dinosaurs once roamed Queensland 160 million years ago -- the biggest of its kind found in Australia.
Savannah Tee
Jun 18, 2020